Treating Brain Aneurysms
Repairing neurological damage from aneurysm, stroke and other brain and spine vascular problems is more promising today thanks to diagnostic, imaging and treatment advances.
In clinic and case conferences, our team of experienced specialists works closely together to develop the best treatment plan, guided by diagnostic imaging, and based on several factors that include:
- Patient age and health
- Size, shape and location of the aneurysm
- Family history of aneurysm
Treatments for Brain Aneurysm
Watchful Waiting
If an aneurysm has not ruptured, and it is very small (a few millimeters in size), doctors may recommend watchful waiting, or observation. Conservative management may be the best approach especially for those who are elderly or have other medical conditions that might increase the risks associated with treatment. Doctors may follow small aneurysms with regular imaging studies to monitor aneurysm growth and changes, and the development of any symptoms. Based on any changes, symptoms or patient preference, doctors may choose to treat the aneurysm.
Surgery
For open surgical treatment of ruptured and unruptured aneurysms, microsurgical clipping is the typical treatment of choice. In rare instances, bypass procedures can be combined with occlusion (closing off) of the aneurysm.
Clipping
After the patient is under anesthesia and asleep, the neurosurgeon removes a section of the skull, uses a microscope to locate the aneurysm, and puts a small titanium clip(s) at the base or neck of the aneurysm. Not unlike a clothespin, the clip pinches the neck of the aneurysm and stops its blood supply. The surgeon replaces the skull and closes the scalp. The clip stays put, the aneurysm shrivels and the long-term prognosis is excellent.
While the surgery itself has changed little in recent years, there have been dramatic advancements in clip technology and application. Today there are increasingly smaller and thinner clips, and our neurosurgeons were among the first in the country to use them. Additionally, thanks to special, very low profile appliers, surgeons can insert these clips through tiny incisions.
ECIC Bypass
When neurosurgeons need to build a new artery to reroute blood around a diseased vessel or aneurysm, or to treat Moya-Moya disease (a tangle of vessels), they do an extracranial-to-intracranial (ECIC) bypass. They take the artery outside of the head on the side of the scalp (the superficial temporal artery), open the skull, and sew it to the artery inside the head.
Or, they may do the bypass using the long saphenous vein from the leg. In this case, they would connect the saphenous vein graft to the carotid artery in the neck, pass it under the skin, and sew it to the middle cerebral artery inside the head.
Endovascular Treatment
An alternative to open surgery, endovascular means “within
the blood vessel.” Endovascular treatment allows doctors to thread special
catheters (tiny tubes) and work through tiny blood vessels in the brain without
having to cut through the scalp and remove a section of the skull.
Physicians perform endovascular treatment for aneurysms and
other brain and spine vascular problems in BIDMC’s arteriography suite. The suite features the latest imaging technologies,
producing crystal clear images in minute detail of blood vessels and blood
flow, and changes brought on by disease.
Endovascular Embolization (Coiling)
One technique for sealing a ruptured or unruptured aneurysm to prevent or stop bleeding. Embolization means blocking off the blood vessel or aneurysm from the inside, using coils or some other material.
While the patient is asleep, the doctor, guided by angiography, threads a thin, hollow tube (a catheter) carrying tiny metal coils through an artery in the groin to the aneurysm in the brain. Then the doctor fills the aneurysm with the coils. The coils cause the blood to clot, which excludes the aneurysm from the circulation.
Although effective, this procedure may need to be done more than once and imaging follow-up is required.
Stents
If the base of the aneurysm is wide or the aneurysm itself is large, doctors may need to use a small stent (a metal mesh device) to hold the coils in place, much like scaffolding. The stent is permanent and stays inside the artery at the neck of the aneurysm.
In some cases, doctors inflate a removable balloon near the aneurysm to help position the coils in the sac. Once the coils are in the sac, doctors deflate and remove the balloon.
Stent design continues to evolve, to better secure coils within large aneurysms, and to be easily retrieved should they need to be recaptured. The stents we use at BIDMC are on technology’s leading edge.
Flow Diverters
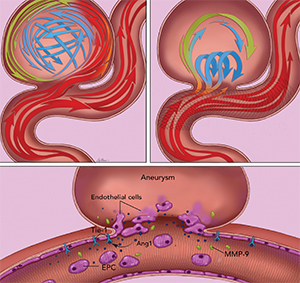 Doctors may treat certain types of aneurysms with flow diverters, like the Pipeline Embolization Device. Positioned via a catheter, just like coils, the Pipeline device is a flexible mesh tube that can block off aneurysms typically found in the carotid artery. This major blood vessel ferries blood to the front of the brain. Once positioned, the Pipeline expands against the artery wall and across the neck of the aneurysm, reducing blood flow to the sac, which eventually clots and shrinks.
Doctors may treat certain types of aneurysms with flow diverters, like the Pipeline Embolization Device. Positioned via a catheter, just like coils, the Pipeline device is a flexible mesh tube that can block off aneurysms typically found in the carotid artery. This major blood vessel ferries blood to the front of the brain. Once positioned, the Pipeline expands against the artery wall and across the neck of the aneurysm, reducing blood flow to the sac, which eventually clots and shrinks.
By redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm sac, flow diverters like the Pipeline may help “remodel” circulation in the parent vessel.
Endovascular Treatment for Arteriovenous Malformations
The Brain Aneurysm Institute also excels at treating arteriovenous malformation (AVM). An AVM is a tangle of blood vessels that create a “short circuit” of sorts, diverting oxygenated blood directly from an artery to a vein, before the oxygen can nourish the surrounding brain or spine tissue. Over time, these weak and abnormal blood vessels can dilate (expand), rupture and bleed.
Based on the type, size and location of the AVM, as well as patient symptoms, treatment can include one or all of the following therapies:
- Surgery to remove the tangle of vessels may be the best approach if the AVM is bleeding and easy to reach.
- Endovascular embolization, blocking the vessels off with coils or glues, could be a multi-step process done over several weeks to isolate and block all of the different arteries that may feed the AVM.
- CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery is very useful if the AVM is in a difficult-to-reach area, and not too large. Focused beams of radiation are necessary to provide a high dose of radiation to the AVM with minimal or no radiation to surrounding brain tissue. However, it can take one to two years for the blood vessels to scar down and close. And during that time, the AVM could bleed.
- Combination treatment using all three modalities is a special area of excellence at BIDMC. Our team works closely together to coordinate the best approach and timing. We are highly experienced in endovascular technique to treat AVMs, and in sorting out the complexities of treatment: which arteries feed the AVM and which can be safely blocked off?
Treatment for Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (DAVF)
DAVF is an abnormal connection between the arteries within the dura mater — the thick membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord — and the veins that drain the brain. If it is not fixed, it can lead to brain hemorrhages or spinal cord malfunction.
The surgical repair is to disconnect the artery from the vein. Our multidisciplinary group excels at performing this repair with endovascular technique; that is, using a minimally invasive approach through the groin artery. However, if the DAVF is deep inside the brain, then CyberKnife is the preferred treatment. Open surgery is also used in carefully selected patients.
Endovascular Treatment for Carotid-Cavernous Fistula (CCF)
CCF is an abnormal connection between an artery in the neck (carotid artery) and the veins behind the eye. These individuals experience eye redness, swelling and congestion that impact their vision.
Our highly skilled multidisciplinary team, using advanced endovascular techniques, can block the abnormal connection between the artery and the veins behind the eye, which reduces congestion and restores sight.
Options for Carotid Body Tumor
Multi-specialty teamwork is also important for treating carotid body tumors. A carotid body tumor is a growth in the carotid artery, the blood vessels in the neck that carry blood to the brain. Neurosurgeons, vascular surgeons, head and neck/otolaryngology (ENT) surgeons, and other physicians and specialists work together to treat these abnormal growths.
Generally the first step, using endovascular technique, is to embolize, or block, the blood vessels that feed the tumor. Without blood, the tumor shrinks. Then, in an open procedure, surgeons can operate to safely remove the abnormal growth. Radiation is also considered as an option in these patients.
 In clinic and case conferences, our team of experienced specialists works closely together to develop the best treatment plan, guided by diagnostic imaging, and based on several factors that include:
In clinic and case conferences, our team of experienced specialists works closely together to develop the best treatment plan, guided by diagnostic imaging, and based on several factors that include:

