Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy
Understanding Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy, or removal of the kidney, may be necessary when patients have recurrent kidney infections, irreversible damage, long-term obstruction or masses suspicious for kidney cancer.
Traditional open surgery involves making an 8-20 inch incision in the flank or abdomen, and in many cases removing a rib. Postoperative pain and numbness near the wound site can interfere with breathing and extend recovery. Laparoscopic nephrectomy, using tiny "keyhole" incisions, offers similar cure rates but with decreased blood loss, shorter hospital stays and recovery, less pain and better cosmetic outcome. (see figure 1a and 1b)
The procedure
Under general anesthesia, trocars (cylindrical tubes) are placed into the
abdominal cavity through 3-5 tiny incisions, from 0.5cm-1cm, to allow
insertion of the laparoscope. Next, carbon dioxide injected through one of
the incisions enlarges the cavity and separates the abdominal wall from
other organs. A laparoscopic camera provides a magnified view, making it
possible to identify vessels and structures more clearly than in open
surgery.
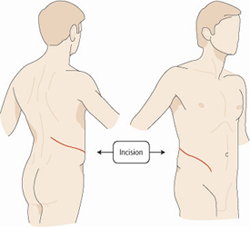
Figure 1a
Traditional open kidney surgery is performed through an 8-12 inch
incision extending from the ribs towards the abdomen. A portion of one
of the ribs is usually removed as part of the surgery.
Thin surgical instruments then are inserted. The ureter and vessels that carry blood to and from the kidney are clipped. Once the kidney is freed from surrounding structures, it is extracted and removed through one of the incisions. The wounds are then closed and sutured.
Minimally invasive surgery is part of BIDMC's multidisciplinary approach to kidney tumors. To learn about the comprehensive treatment options available through our Renal Tumor Clinic, please click here.
Advantages over open surgery
-
Improved visualization of surgical field
- Less blood loss
- Less pain
- Shorter hospital stay
- Quicker recovery
- Better cosmetic result
Results
Cancer control
Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy controls cancer equally as well as the traditional open procedure.
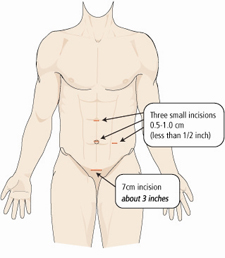
Figure 1b
Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy is performed through 3 small incisions in
the abdomen. The kidney and tumor are removed through a horizontal incision
(usually about 3 inches) in the lower abdomen.
Blood loss
Typical blood loss is 100-200cc. Blood transfusions are extremely rare."
What to expect after surgery
Hospital stay
The typical hospital stay is 2 days.
Diet
A clear liquid diet is started the day after surgery and a regular diet on
the second day.
Postoperative pain
Pain is managed immediately with an intravenous patient controlled analgesia pump, which is removed and replaced by pills the day after surgery. Upon discharge, pain pills are given for several days, after which over-the-counter acetaminophen or ibuprofen are usually all that is needed.
Urinary catheter
A urinary catheter is left in place for 1 day following the surgery and then removed.
Recovery
Most patients are able to return to full activity within 3-4 weeks compared with 8-12 weeks for open radical nephrectomy.
Follow-up
Patients will follow-up with their surgeon 1 month after the operation for a routine visit. Appointments can easily be conducted over the phone for patients living outside the Boston area, including international patients.
